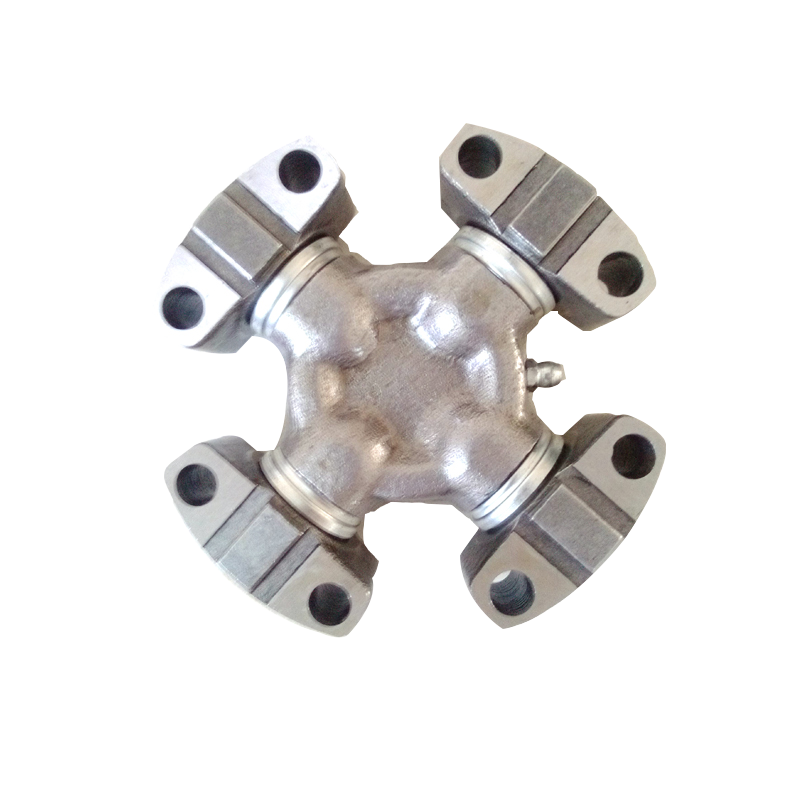
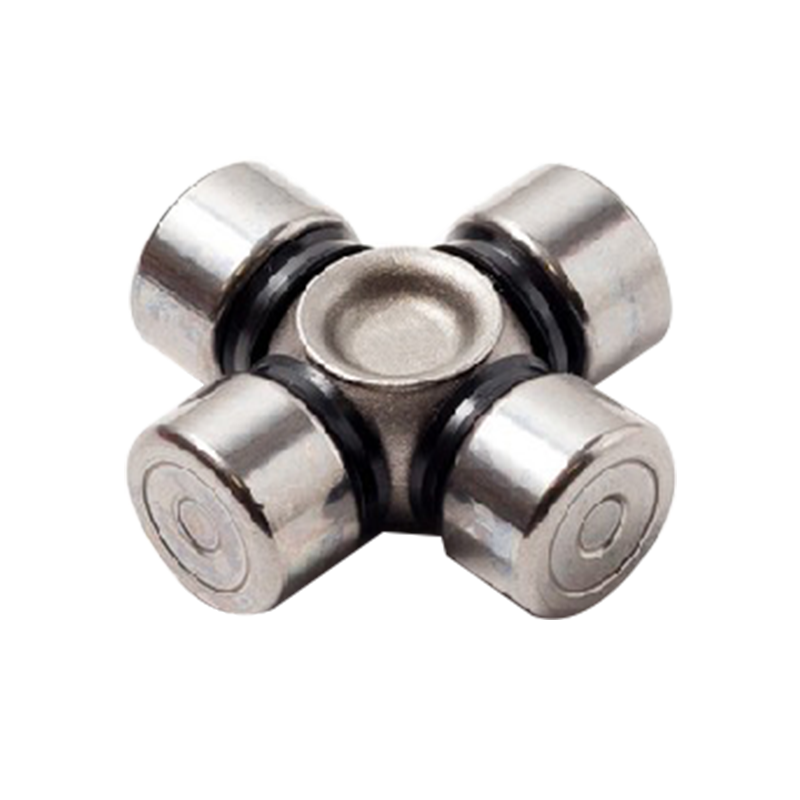
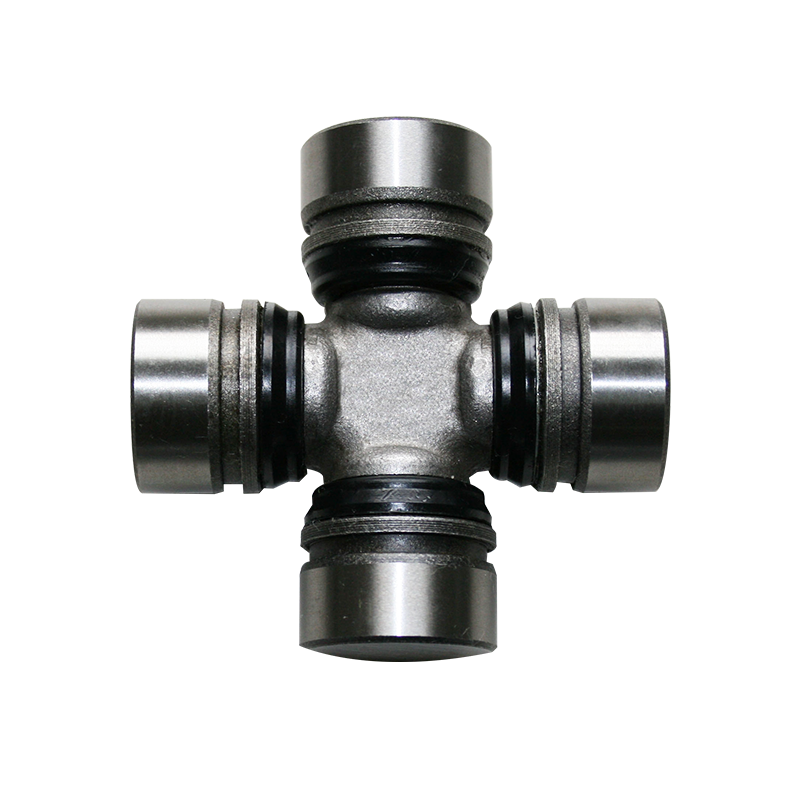
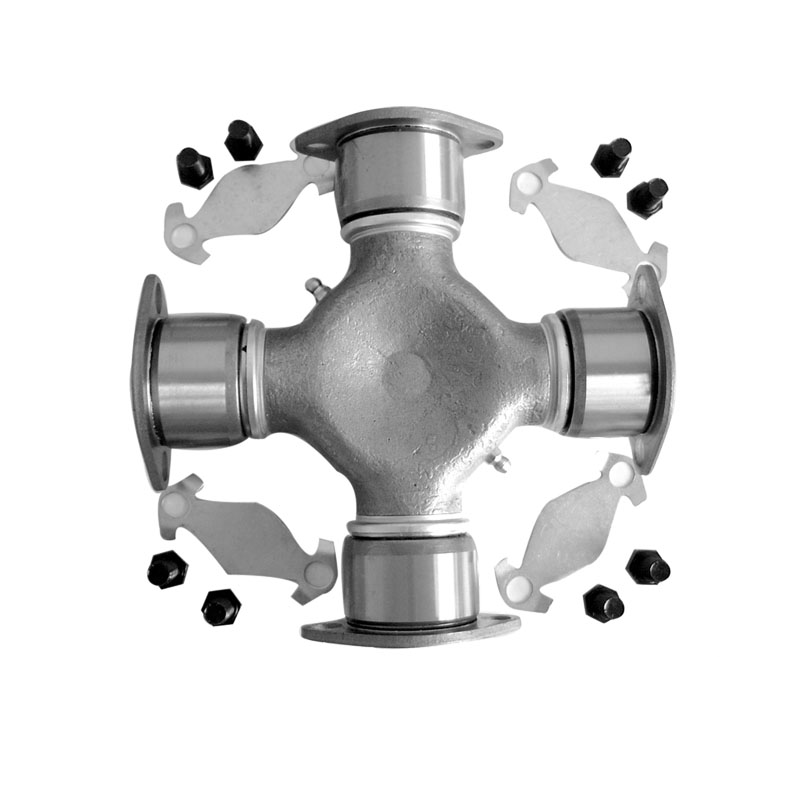
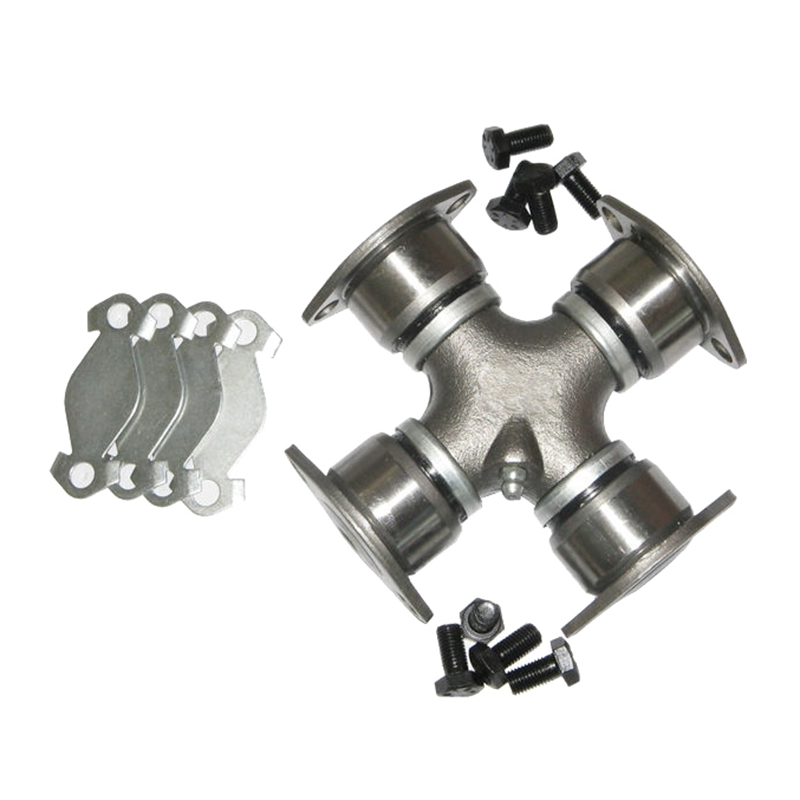
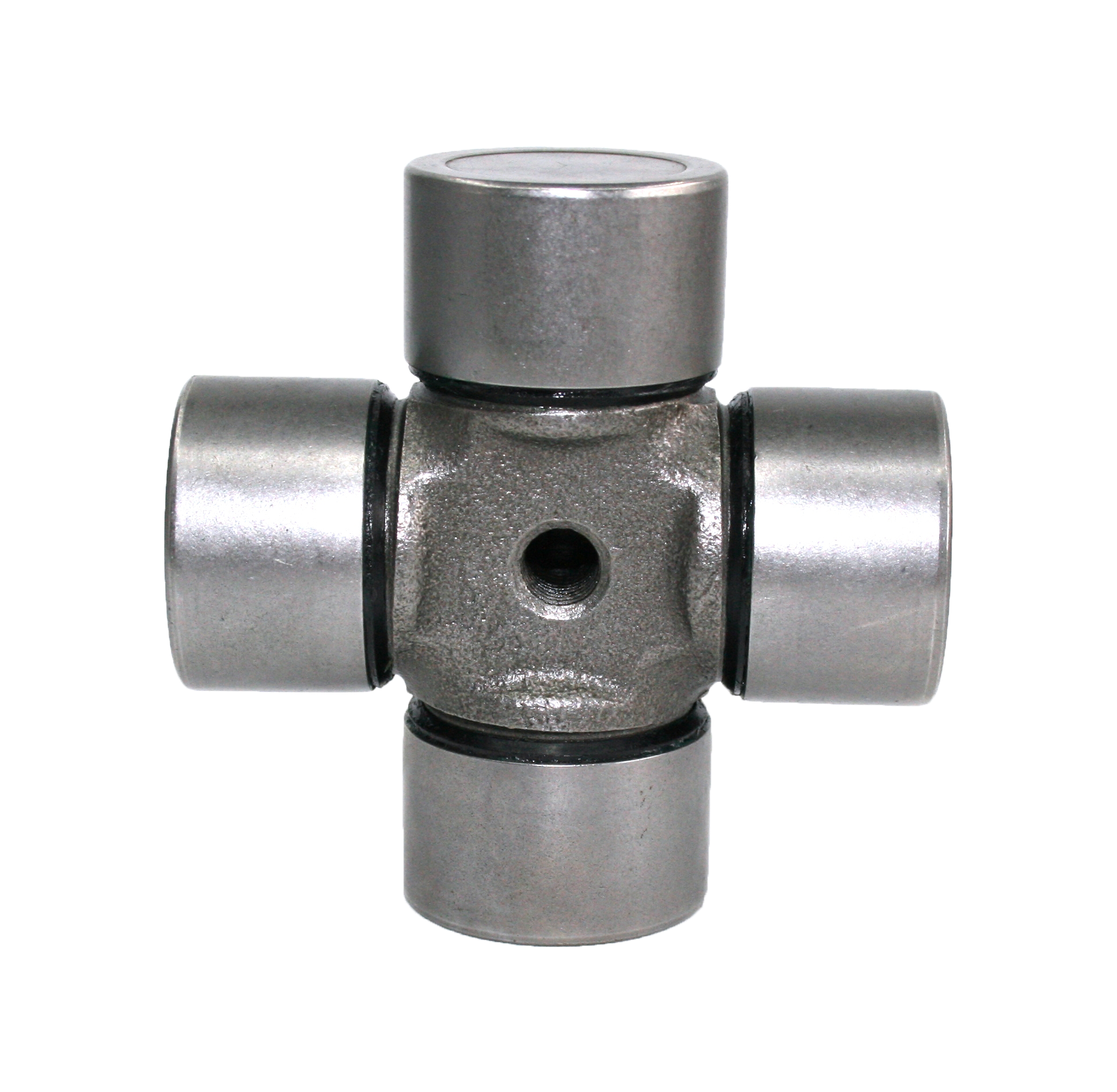
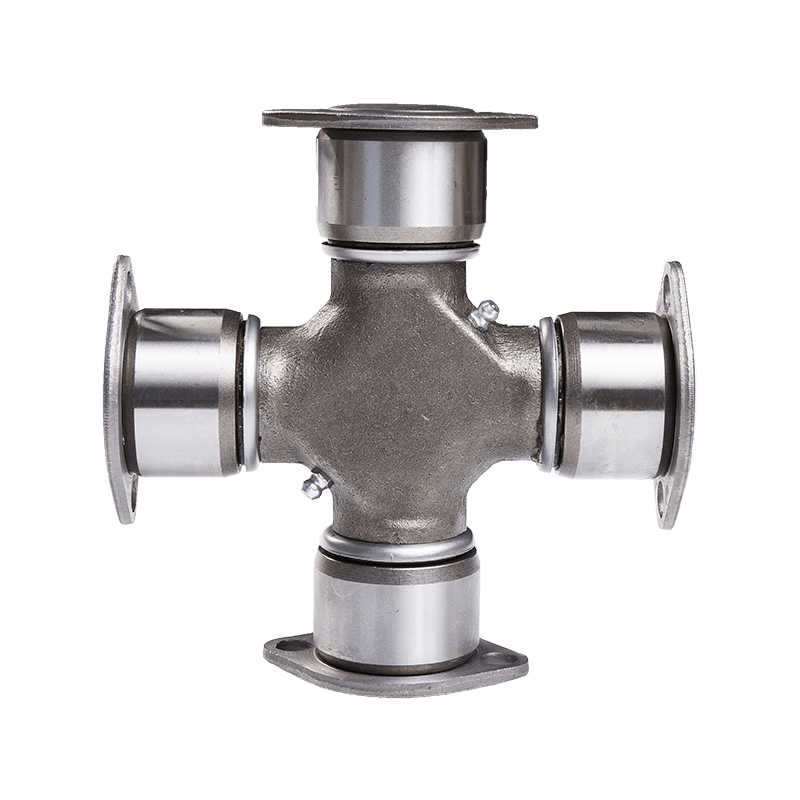
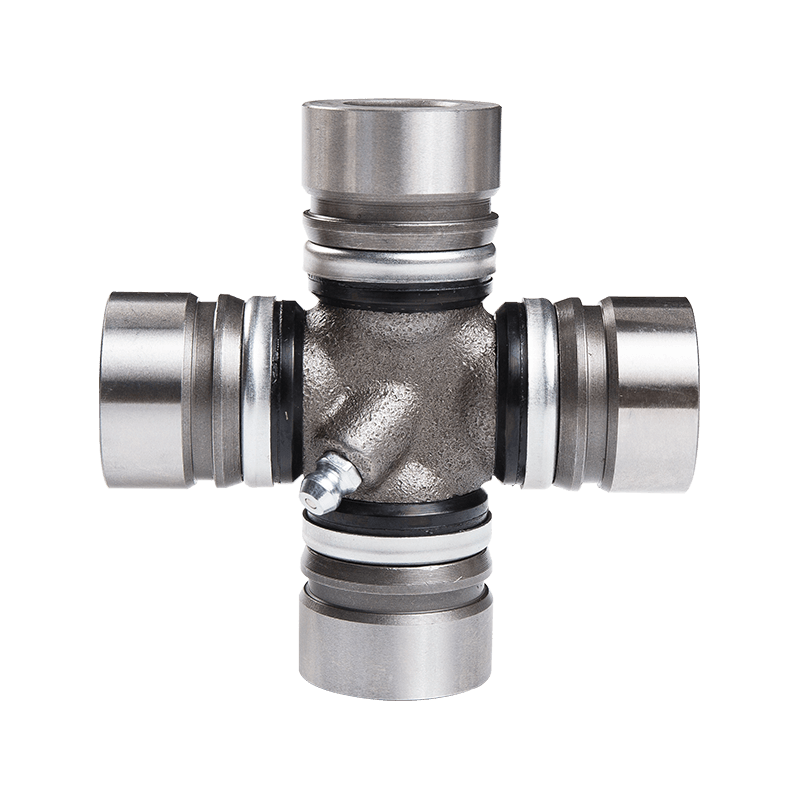
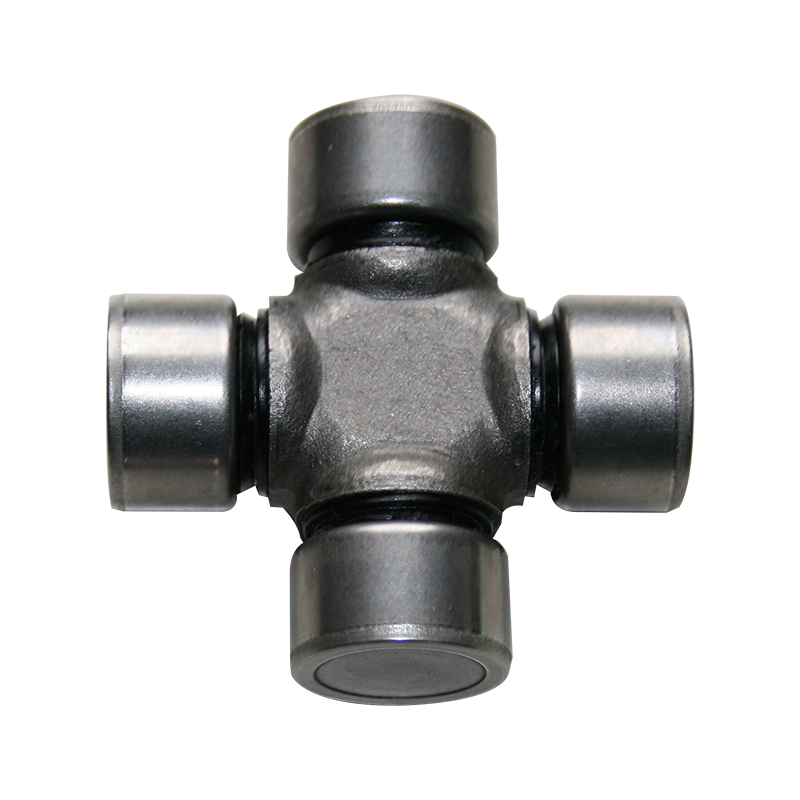
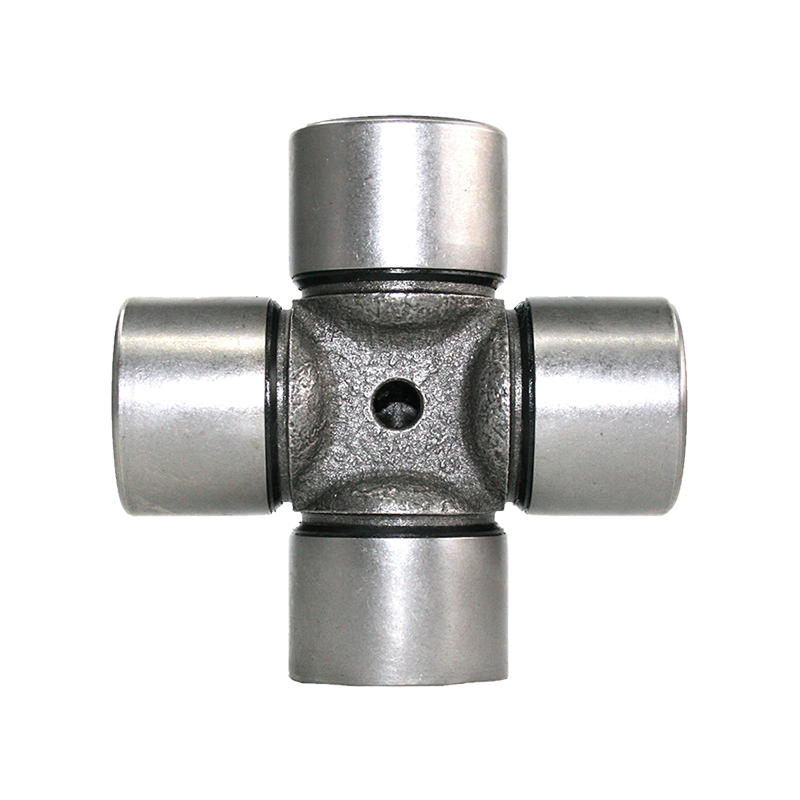
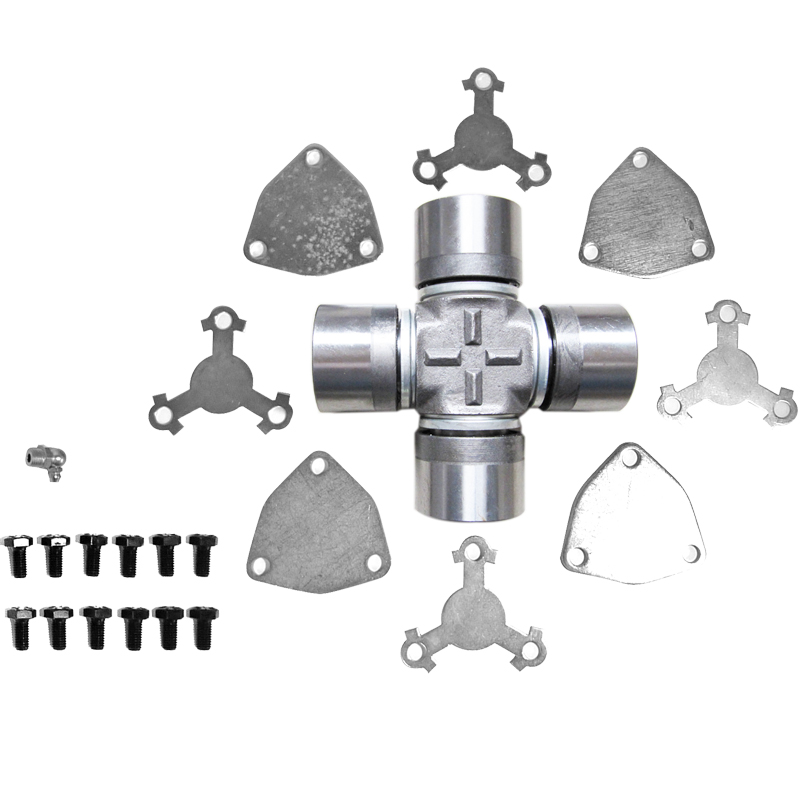
Steering System Universal Joint ST1638 Maintenance Free How do you seal a joint to prevent contamination or debris from entering?
Sealing a
Steering System Universal Joint ST1638 Maintenance Free to prevent contamination or debris from entering involves utilizing various specialized sealing methods and components to ensure a barrier against external elements. Here are some common techniques used to seal these joints effectively:
Seal Design and Material: Utilization of high-quality seal materials, often rubber or advanced polymers, that are durable, flexible, and resistant to environmental factors. These seals are designed to create a protective barrier around the joint components.
Boot or Protective Cover: Using a protective boot or cover made from rubber or similar materials that encapsulates the joint, shielding it from dust, moisture, and debris. This cover moves with the joint's motion while maintaining a protective barrier.
Precision Machining and Tight Tolerances: Precision engineering and tight assembly tolerances are crucial. Precision machining ensures that the joint components fit together tightly, leaving minimal gaps where contaminants could enter.
Specialized Sealing Technologies: Some maintenance-free joints may integrate advanced sealing technologies such as double lip seals, labyrinth seals, or other proprietary designs. These innovative seals create more effective barriers against contaminants.
Integrated Lubricant Seals: Certain joints might have specialized seals to retain internal lubrication while preventing external contaminants from entering. This aids in maintaining smooth operation while safeguarding the joint from debris.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance Checks: Even though these joints are designed to be maintenance-free, periodic inspections are essential to ensure the seals remain intact and effective. Regular checks help identify any wear, tears, or damage to the seals that might compromise their function.
How does the Steering System Universal Joint ST1638 Maintenance Free respond to environmental factors such as moisture, dust or temperature changes?
Moisture Resistance:
Sealed Design: Maintenance-free joints often feature protective seals or boots made from materials that are moisture-resistant. These seals act as a barrier, preventing moisture from entering the joint, thus reducing the risk of corrosion and potential damage to internal components.
Corrosion Resistance: The materials used in the joint's construction are often chosen for their resistance to corrosion, ensuring that moisture exposure does not degrade the joint's structural integrity.
Dust and Debris Protection:
Protective Enclosure: The boots or covers enclosing the joint components act as a shield against dust, dirt, and debris, minimizing their entry and accumulation within the joint.
Sealing Mechanisms: Advanced sealing technologies, such as double lip seals or labyrinth seals, help to further prevent dust and debris ingress, maintaining the joint's functionality.
Temperature Changes:
Material Selection: The materials used in maintenance-free joints are often chosen for their ability to withstand a range of temperatures. These materials can handle both high and low-temperature conditions without significantly affecting the joint's performance.
Thermal Expansion Consideration: The design accounts for thermal expansion and contraction to ensure the joint operates smoothly even during temperature fluctuations.

 English
English Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体